
자바로 작성된 팩토리 메서드
팩토리 메서드는 제품 객체들의 구상 클래스들을 지정하지 않고 해당 제품 객체들을 생성할 수 있도록 하는 생성 디자인 패턴입니다.
팩토리 메서드는 메서드를 정의하며, 이 메서드는 직접 생성자 호출(new 연산자)을 사용하여 객체를 생성하는 대신 객체 생성에 사용되여야 합니다. 자식 클래스들은 이 메서드를 오버라이드하여 생성될 객체들의 클래스를 변경할 수 있습니다.
다양한 팩토리 패턴들과 개념들의 차이점을 이해하지 못하셨다면 팩토리 비교를 읽어보세요.
복잡도:
인기도:
사용 사례들: 팩토리 메서드 패턴은 자바 코드에서 널리 사용되며 코드에 높은 수준의 유연성을 제공해야 할 때 매우 유용합니다.
이 패턴은 핵심 자바 라이브러리에 등장합니다:
java.util.Calendar#getInstance()java.util.ResourceBundle#getBundle()java.text.NumberFormat#getInstance()java.nio.charset.Charset#forName()java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory#createURLStreamHandler(String)(프로토콜에 따라 다른 싱글턴 객체를 반환합니다.)java.util.EnumSet#of()javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext#createMarshaller()와 다른 유사한 메서드들.
식별: 팩토리 메서드는 구상 클래스들로부터 객체들을 생성하는 생성 메서드들로 인식될 수 있습니다. 구상 클래스들은 객체 생성 중에 사용되지만 팩토리 메서드들의 반환 유형은 일반적으로 추상 클래스 또는 인터페이스로 선언됩니다.
크로스 플랫폼 그래픽 사용자 요소들의 생성
이 예시에서는 버튼들은 제품의 역할을 하고 다이얼로그들은 크리에이터의 역할을 합니다.
각 다른 다이얼로그 유형은 그의 고유한 요소 유형들이 필요합니다. 그러므로 각 다이얼로그 유형에 대한 자식 클래스를 만들고 해당 팩토리 메서드들을 오버라이드합니다.
이제 각 다이얼로그 유형은 적절한 버튼 클래스들을 인스턴스화할 것입니다. 기초 다이얼로그는 공통 인터페이스를 사용하는 제품과 함께 작동하므로 모든 변경 후에도 해당 기초 다이얼로그의 코드가 계속 작동할 것입니다.
buttons
buttons/Button.java: 공통 제품 인터페이스
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons;
/**
* Common interface for all buttons.
*/
public interface Button {
void render();
void onClick();
}
buttons/HtmlButton.java: 구상 제품
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons;
/**
* HTML button implementation.
*/
public class HtmlButton implements Button {
public void render() {
System.out.println("<button>Test Button</button>");
onClick();
}
public void onClick() {
System.out.println("Click! Button says - 'Hello World!'");
}
}
buttons/WindowsButton.java: 또 하나의 구상 제품
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
/**
* Windows button implementation.
*/
public class WindowsButton implements Button {
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JButton button;
public void render() {
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JLabel label = new JLabel("Hello World!");
label.setOpaque(true);
label.setBackground(new Color(235, 233, 126));
label.setFont(new Font("Dialog", Font.BOLD, 44));
label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
panel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
frame.getContentPane().add(panel);
panel.add(label);
onClick();
panel.add(button);
frame.setSize(320, 200);
frame.setVisible(true);
onClick();
}
public void onClick() {
button = new JButton("Exit");
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
frame.setVisible(false);
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
factory
factory/Dialog.java: 기초 크리에이터
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons.Button;
/**
* Base factory class. Note that "factory" is merely a role for the class. It
* should have some core business logic which needs different products to be
* created.
*/
public abstract class Dialog {
public void renderWindow() {
// ... other code ...
Button okButton = createButton();
okButton.render();
}
/**
* Subclasses will override this method in order to create specific button
* objects.
*/
public abstract Button createButton();
}
factory/HtmlDialog.java: 구상 크리에이터
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons.Button;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons.HtmlButton;
/**
* HTML Dialog will produce HTML buttons.
*/
public class HtmlDialog extends Dialog {
@Override
public Button createButton() {
return new HtmlButton();
}
}
factory/WindowsDialog.java: 또 하나의 구상 크리에이터
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons.Button;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.buttons.WindowsButton;
/**
* Windows Dialog will produce Windows buttons.
*/
public class WindowsDialog extends Dialog {
@Override
public Button createButton() {
return new WindowsButton();
}
}
Demo.java: 클라이언트 코드
package refactoring_guru.factory_method.example;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory.Dialog;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory.HtmlDialog;
import refactoring_guru.factory_method.example.factory.WindowsDialog;
/**
* Demo class. Everything comes together here.
*/
public class Demo {
private static Dialog dialog;
public static void main(String[] args) {
configure();
runBusinessLogic();
}
/**
* The concrete factory is usually chosen depending on configuration or
* environment options.
*/
static void configure() {
if (System.getProperty("os.name").equals("Windows 10")) {
dialog = new WindowsDialog();
} else {
dialog = new HtmlDialog();
}
}
/**
* All of the client code should work with factories and products through
* abstract interfaces. This way it does not care which factory it works
* with and what kind of product it returns.
*/
static void runBusinessLogic() {
dialog.renderWindow();
}
}
OutputDemo.txt: 실행 결과 (HtmlDialog)
<button>Test Button</button>
Click! Button says - 'Hello World!'
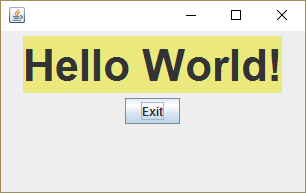
OutputDemo.png: 실행 결과 (WindowsDialog)
 겨울 세일 마감 임박!
겨울 세일 마감 임박!
