Composite en Java
Le Composite est un patron de conception structurel qui permet d’agencer les objets dans une structure ressemblant à une arborescence, afin de pouvoir la traiter comme un objet individuel.
Le composite est devenu la solution la plus populaire pour régler les problèmes d’une structure arborescente. Il offre une fonctionnalité très pratique qui permet de parcourir récursivement toute l’arborescence et d’additionner les résultats.
Complexité :
Popularité :
Exemples d’utilisation : Le composite est très répandu en Java. Il est souvent utilisé pour modéliser les hiérarchies des composants d’une interface utilisateur ou pour du code qui manipule des graphes.
Voici quelques exemples tirés des bibliothèques standards de Java :
-
java.awt.Container#add(Component)(dans pratiquement tous les composants Swing) -
javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren()(dans pratiquement tous les composants de JSF UI)
Identification : Si vous avez une arborescence composée uniquement d’objets issus de la même hiérarchie de classes, c’est probablement un composite. Si les méthodes de ces classes délèguent les tâches aux objets enfants de l’arborescence et passent par une classe de base ou interface de la hiérarchie pour ce faire, il est très probable que ce soit véritablement un composite.
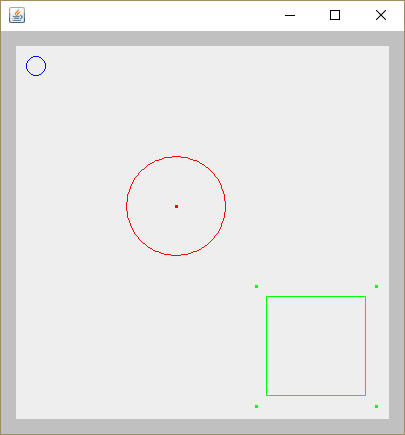
Formes graphiques simples et composées
Dans cet exemple, vous pouvez voir comment créer des formes graphiques complexes, composées de formes graphiques plus simples, et les traiter toutes uniformément.
shapes
shapes/Shape.java: Interface commune aux formes
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public interface Shape {
int getX();
int getY();
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void move(int x, int y);
boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y);
void select();
void unSelect();
boolean isSelected();
void paint(Graphics graphics);
}
shapes/BaseShape.java: Classe Forme abstraite avec fonctionnalités basiques
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
abstract class BaseShape implements Shape {
public int x;
public int y;
public Color color;
private boolean selected = false;
BaseShape(int x, int y, Color color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public int getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
return x > getX() && x < (getX() + getWidth()) &&
y > getY() && y < (getY() + getHeight());
}
@Override
public void select() {
selected = true;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
selected = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isSelected() {
return selected;
}
void enableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
float[] dash1 = {2.0f};
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1.0f,
BasicStroke.CAP_BUTT,
BasicStroke.JOIN_MITER,
2.0f, dash1, 0.0f));
}
void disableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(color);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
else {
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
// ...
}
}
shapes/Dot.java: Un point
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Dot extends BaseShape {
private final int DOT_SIZE = 3;
public Dot(int x, int y, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.fillRect(x - 1, y - 1, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
}
shapes/Circle.java: Un cercle
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Circle extends BaseShape {
public int radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawOval(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/Rectangle.java: Un rectangle
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Rectangle extends BaseShape {
public int width;
public int height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/CompoundShape.java: Forme composée, constituée d’autres objets forme
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CompoundShape extends BaseShape {
protected List<Shape> children = new ArrayList<>();
public CompoundShape(Shape... components) {
super(0, 0, Color.BLACK);
add(components);
}
public void add(Shape component) {
children.add(component);
}
public void add(Shape... components) {
children.addAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void remove(Shape child) {
children.remove(child);
}
public void remove(Shape... components) {
children.removeAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void clear() {
children.clear();
}
@Override
public int getX() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = children.get(0).getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getX() < x) {
x = child.getX();
}
}
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int y = children.get(0).getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getY() < y) {
y = child.getY();
}
}
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
int maxWidth = 0;
int x = getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeX = child.getX() - x;
int childWidth = childsRelativeX + child.getWidth();
if (childWidth > maxWidth) {
maxWidth = childWidth;
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
int maxHeight = 0;
int y = getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeY = child.getY() - y;
int childHeight = childsRelativeY + child.getHeight();
if (childHeight > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = childHeight;
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
child.move(x, y);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
super.unSelect();
for (Shape child : children) {
child.unSelect();
}
}
public boolean selectChildAt(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
child.select();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(getX() - 1, getY() - 1, getWidth() + 1, getHeight() + 1);
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
for (Shape child : children) {
child.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
editor
editor/ImageEditor.java: Éditeur de formes
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Shape;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.Border;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
public class ImageEditor {
private EditorCanvas canvas;
private CompoundShape allShapes = new CompoundShape();
public ImageEditor() {
canvas = new EditorCanvas();
}
public void loadShapes(Shape... shapes) {
allShapes.clear();
allShapes.add(shapes);
canvas.refresh();
}
private class EditorCanvas extends Canvas {
JFrame frame;
private static final int PADDING = 10;
EditorCanvas() {
createFrame();
refresh();
addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
allShapes.unSelect();
allShapes.selectChildAt(e.getX(), e.getY());
e.getComponent().repaint();
}
});
}
void createFrame() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
Border padding = BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(PADDING, PADDING, PADDING, PADDING);
contentPanel.setBorder(padding);
frame.setContentPane(contentPanel);
frame.add(this);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
}
public int getWidth() {
return allShapes.getX() + allShapes.getWidth() + PADDING;
}
public int getHeight() {
return allShapes.getY() + allShapes.getHeight() + PADDING;
}
void refresh() {
this.setSize(getWidth(), getHeight());
frame.pack();
}
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
allShapes.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
Demo.java: Code client
package refactoring_guru.composite.example;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor.ImageEditor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Circle;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Dot;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Rectangle;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImageEditor editor = new ImageEditor();
editor.loadShapes(
new Circle(10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE),
new CompoundShape(
new Circle(110, 110, 50, Color.RED),
new Dot(160, 160, Color.RED)
),
new CompoundShape(
new Rectangle(250, 250, 100, 100, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 240, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 240, Color.GREEN)
)
);
}
}
OutputDemo.png: Résultat de l’exécution