Composite を Java で
Composite は、 構造に関するデザインパターンの一つで、 オブジェクトを木のような構造に構成し、 あたかも単一のオブジェクトであるかのように扱えるようにします。
Composite は、 ツリー構造の構築を必要とする問題の大部分の解決策として、 かなりの人気を得るようになりました。 Composite の大きな特徴は、 ツリー構造全体でメソッドを再帰的に実行し、 結果をまとめあげることです。
複雑度:
人気度:
使用例: Composite パターンは、 Java コードではよく見かけます。 ユーザー・インターフェースのコンポーネントの階層構造の表現や、 グラフに対して動作するコードで多く使われます。
Java の標準ライブラリーでの Composite の使用例です:
-
java.awt.Container#add(Component)(実質的に Swing コンポーネントのいたるところで) -
javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren()(実質的に JSF の UI コンポーネントのいたるところで)
見つけ方: オブジェクト・ツリーがあって、 ツリーのそれぞれのオブジェクトが同じクラス階層の部分であれば、 十中八九、 コンポジットです。 もしこれらのクラス中のメソッドが、 ツリーの子オブジェクトに仕事を委任し、 それを階層の基底クラスやインターフェースを介して行うなら、 これは間違いなくコンポジットです。
単純な形状と複合形状
この例は、 単純な形状からなる複雑な形状をどう作成し、 単純形状と複合形状をどう同様に扱うかを示します。
shapes
shapes/Shape.java: 共通の形状インターフェース
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public interface Shape {
int getX();
int getY();
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void move(int x, int y);
boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y);
void select();
void unSelect();
boolean isSelected();
void paint(Graphics graphics);
}
shapes/BaseShape.java: 基本的な機能を持った抽象的形状
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
abstract class BaseShape implements Shape {
public int x;
public int y;
public Color color;
private boolean selected = false;
BaseShape(int x, int y, Color color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public int getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
return x > getX() && x < (getX() + getWidth()) &&
y > getY() && y < (getY() + getHeight());
}
@Override
public void select() {
selected = true;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
selected = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isSelected() {
return selected;
}
void enableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
float[] dash1 = {2.0f};
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1.0f,
BasicStroke.CAP_BUTT,
BasicStroke.JOIN_MITER,
2.0f, dash1, 0.0f));
}
void disableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(color);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
else {
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
// ...
}
}
shapes/Dot.java: 点
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Dot extends BaseShape {
private final int DOT_SIZE = 3;
public Dot(int x, int y, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.fillRect(x - 1, y - 1, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
}
shapes/Circle.java: 円
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Circle extends BaseShape {
public int radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawOval(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/Rectangle.java: 四角形
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Rectangle extends BaseShape {
public int width;
public int height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/CompoundShape.java: 他の形状オブジェクトから構成される複合形状
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CompoundShape extends BaseShape {
protected List<Shape> children = new ArrayList<>();
public CompoundShape(Shape... components) {
super(0, 0, Color.BLACK);
add(components);
}
public void add(Shape component) {
children.add(component);
}
public void add(Shape... components) {
children.addAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void remove(Shape child) {
children.remove(child);
}
public void remove(Shape... components) {
children.removeAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void clear() {
children.clear();
}
@Override
public int getX() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = children.get(0).getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getX() < x) {
x = child.getX();
}
}
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int y = children.get(0).getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getY() < y) {
y = child.getY();
}
}
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
int maxWidth = 0;
int x = getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeX = child.getX() - x;
int childWidth = childsRelativeX + child.getWidth();
if (childWidth > maxWidth) {
maxWidth = childWidth;
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
int maxHeight = 0;
int y = getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeY = child.getY() - y;
int childHeight = childsRelativeY + child.getHeight();
if (childHeight > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = childHeight;
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
child.move(x, y);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
super.unSelect();
for (Shape child : children) {
child.unSelect();
}
}
public boolean selectChildAt(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
child.select();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(getX() - 1, getY() - 1, getWidth() + 1, getHeight() + 1);
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
for (Shape child : children) {
child.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
editor
editor/ImageEditor.java: 形状エディター
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Shape;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.Border;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
public class ImageEditor {
private EditorCanvas canvas;
private CompoundShape allShapes = new CompoundShape();
public ImageEditor() {
canvas = new EditorCanvas();
}
public void loadShapes(Shape... shapes) {
allShapes.clear();
allShapes.add(shapes);
canvas.refresh();
}
private class EditorCanvas extends Canvas {
JFrame frame;
private static final int PADDING = 10;
EditorCanvas() {
createFrame();
refresh();
addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
allShapes.unSelect();
allShapes.selectChildAt(e.getX(), e.getY());
e.getComponent().repaint();
}
});
}
void createFrame() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
Border padding = BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(PADDING, PADDING, PADDING, PADDING);
contentPanel.setBorder(padding);
frame.setContentPane(contentPanel);
frame.add(this);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
}
public int getWidth() {
return allShapes.getX() + allShapes.getWidth() + PADDING;
}
public int getHeight() {
return allShapes.getY() + allShapes.getHeight() + PADDING;
}
void refresh() {
this.setSize(getWidth(), getHeight());
frame.pack();
}
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
allShapes.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
Demo.java: クライアント・コード
package refactoring_guru.composite.example;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor.ImageEditor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Circle;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Dot;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Rectangle;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImageEditor editor = new ImageEditor();
editor.loadShapes(
new Circle(10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE),
new CompoundShape(
new Circle(110, 110, 50, Color.RED),
new Dot(160, 160, Color.RED)
),
new CompoundShape(
new Rectangle(250, 250, 100, 100, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 240, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 240, Color.GREEN)
)
);
}
}
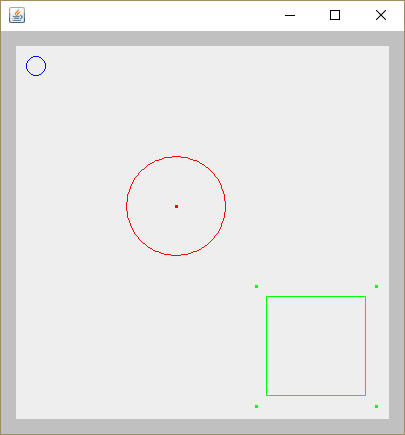
OutputDemo.png: 実行結果