Composite en Java
Composite es un patrón de diseño estructural que permite componer objetos en una estructura en forma de árbol y trabajar con ella como si fuera un objeto único.
El patrón Composite se convirtió en una solución muy popular para la mayoría de problemas que requieren la creación de una estructura de árbol. La gran característica del Composite es la capacidad para ejecutar métodos de forma recursiva por toda la estructura de árbol y recapitular los resultados.
Complejidad:
Popularidad:
Ejemplos de uso: El patrón Composite es muy común en el código Java. Se utiliza a menudo para representar jerarquías de componentes de interfaz de usuario o el código que trabaja con gráficos.
Aquí tienes algunos ejemplos del patrón Composite en las principales bibliotecas de Java:
-
java.awt.Container#add(Component)(prácticamente por todos los componentes Swing) -
javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren()(prácticamente por todos los componentes JSF UI)
Identificación: Si tienes un árbol de objetos y cada objeto de un árbol es parte de la misma jerarquía de clases, lo más probable es que se trate de un compuesto (composite). Si los métodos de estas clases delegan el trabajo de objetos hijos del árbol y lo hacen a través de la clase base/interfaz de la jerarquía, sin duda, se trata de un compuesto.
Formas gráficas simples y compuestas
Este ejemplo muestra cómo crear formas gráficas complejas compuestas por formas simples, y cómo tratarlas a ambas de manera uniforme.
shapes
shapes/Shape.java: Interfaz común de las formas
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public interface Shape {
int getX();
int getY();
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void move(int x, int y);
boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y);
void select();
void unSelect();
boolean isSelected();
void paint(Graphics graphics);
}
shapes/BaseShape.java: Forma abstracta con funcionalidad básica
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
abstract class BaseShape implements Shape {
public int x;
public int y;
public Color color;
private boolean selected = false;
BaseShape(int x, int y, Color color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public int getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
return x > getX() && x < (getX() + getWidth()) &&
y > getY() && y < (getY() + getHeight());
}
@Override
public void select() {
selected = true;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
selected = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isSelected() {
return selected;
}
void enableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
float[] dash1 = {2.0f};
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1.0f,
BasicStroke.CAP_BUTT,
BasicStroke.JOIN_MITER,
2.0f, dash1, 0.0f));
}
void disableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(color);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
else {
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
// ...
}
}
shapes/Dot.java: Un punto
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Dot extends BaseShape {
private final int DOT_SIZE = 3;
public Dot(int x, int y, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.fillRect(x - 1, y - 1, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
}
shapes/Circle.java: Un círculo
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Circle extends BaseShape {
public int radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawOval(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/Rectangle.java: Un rectángulo
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Rectangle extends BaseShape {
public int width;
public int height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/CompoundShape.java: Forma compuesta, que consiste en otros objetos de forma
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CompoundShape extends BaseShape {
protected List<Shape> children = new ArrayList<>();
public CompoundShape(Shape... components) {
super(0, 0, Color.BLACK);
add(components);
}
public void add(Shape component) {
children.add(component);
}
public void add(Shape... components) {
children.addAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void remove(Shape child) {
children.remove(child);
}
public void remove(Shape... components) {
children.removeAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void clear() {
children.clear();
}
@Override
public int getX() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = children.get(0).getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getX() < x) {
x = child.getX();
}
}
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int y = children.get(0).getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getY() < y) {
y = child.getY();
}
}
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
int maxWidth = 0;
int x = getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeX = child.getX() - x;
int childWidth = childsRelativeX + child.getWidth();
if (childWidth > maxWidth) {
maxWidth = childWidth;
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
int maxHeight = 0;
int y = getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeY = child.getY() - y;
int childHeight = childsRelativeY + child.getHeight();
if (childHeight > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = childHeight;
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
child.move(x, y);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
super.unSelect();
for (Shape child : children) {
child.unSelect();
}
}
public boolean selectChildAt(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
child.select();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(getX() - 1, getY() - 1, getWidth() + 1, getHeight() + 1);
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
for (Shape child : children) {
child.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
editor
editor/ImageEditor.java: Editor de forma
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Shape;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.Border;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
public class ImageEditor {
private EditorCanvas canvas;
private CompoundShape allShapes = new CompoundShape();
public ImageEditor() {
canvas = new EditorCanvas();
}
public void loadShapes(Shape... shapes) {
allShapes.clear();
allShapes.add(shapes);
canvas.refresh();
}
private class EditorCanvas extends Canvas {
JFrame frame;
private static final int PADDING = 10;
EditorCanvas() {
createFrame();
refresh();
addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
allShapes.unSelect();
allShapes.selectChildAt(e.getX(), e.getY());
e.getComponent().repaint();
}
});
}
void createFrame() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
Border padding = BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(PADDING, PADDING, PADDING, PADDING);
contentPanel.setBorder(padding);
frame.setContentPane(contentPanel);
frame.add(this);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
}
public int getWidth() {
return allShapes.getX() + allShapes.getWidth() + PADDING;
}
public int getHeight() {
return allShapes.getY() + allShapes.getHeight() + PADDING;
}
void refresh() {
this.setSize(getWidth(), getHeight());
frame.pack();
}
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
allShapes.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
Demo.java: Código cliente
package refactoring_guru.composite.example;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor.ImageEditor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Circle;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Dot;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Rectangle;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo {
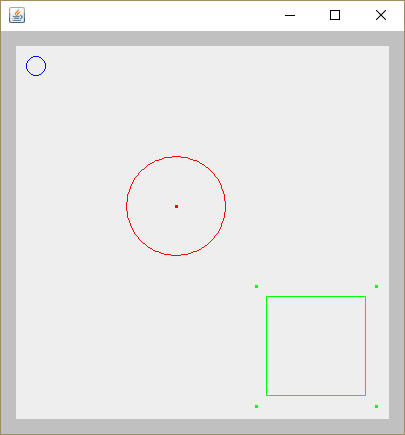
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImageEditor editor = new ImageEditor();
editor.loadShapes(
new Circle(10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE),
new CompoundShape(
new Circle(110, 110, 50, Color.RED),
new Dot(160, 160, Color.RED)
),
new CompoundShape(
new Rectangle(250, 250, 100, 100, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 240, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 240, Color.GREEN)
)
);
}
}
OutputDemo.png: Resultado de la ejecución