Composite in Java
Composite is a structural design pattern that lets you compose objects into tree structures and then work with these structures as if they were individual objects.
Composite became a pretty popular solution for the most problems that require building a tree structure. Composite’s great feature is the ability to run methods recursively over the whole tree structure and sum up the results.
Complexity:
Popularity:
Usage examples: The Composite pattern is pretty common in Java code. It’s often used to represent hierarchies of user interface components or the code that works with graphs.
Here are some composite examples from standard Java libraries:
-
java.awt.Container#add(Component)(practically all over Swing components) -
javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren()(practically all over JSF UI components)
Identification: If you have an object tree, and each object of a tree is a part of the same class hierarchy, this is most likely a composite. If methods of these classes delegate the work to child objects of the tree and do it via the base class/interface of the hierarchy, this is definitely a composite.
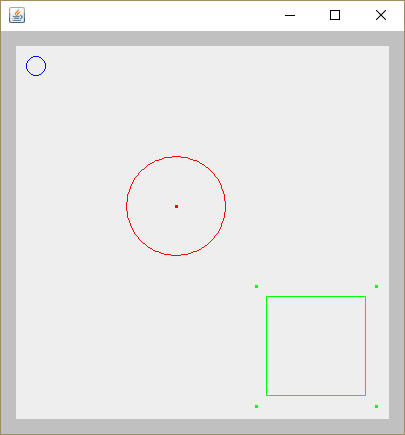
Simple and compound graphical shapes
This example shows how to create complex graphical shapes, composed of simpler shapes and treat both of them uniformly.
shapes
shapes/Shape.java: Common shape interface
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public interface Shape {
int getX();
int getY();
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void move(int x, int y);
boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y);
void select();
void unSelect();
boolean isSelected();
void paint(Graphics graphics);
}
shapes/BaseShape.java: Abstract shape with basic functionality
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
abstract class BaseShape implements Shape {
public int x;
public int y;
public Color color;
private boolean selected = false;
BaseShape(int x, int y, Color color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public int getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
return x > getX() && x < (getX() + getWidth()) &&
y > getY() && y < (getY() + getHeight());
}
@Override
public void select() {
selected = true;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
selected = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isSelected() {
return selected;
}
void enableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
float[] dash1 = {2.0f};
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1.0f,
BasicStroke.CAP_BUTT,
BasicStroke.JOIN_MITER,
2.0f, dash1, 0.0f));
}
void disableSelectionStyle(Graphics graphics) {
graphics.setColor(color);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) graphics;
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
else {
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
// ...
}
}
shapes/Dot.java: A dot
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Dot extends BaseShape {
private final int DOT_SIZE = 3;
public Dot(int x, int y, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return DOT_SIZE;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.fillRect(x - 1, y - 1, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
}
shapes/Circle.java: A circle
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Circle extends BaseShape {
public int radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return radius * 2;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawOval(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/Rectangle.java: A rectangle
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
public class Rectangle extends BaseShape {
public int width;
public int height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, Color color) {
super(x, y, color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
super.paint(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(x, y, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1);
}
}
shapes/CompoundShape.java: Compound shape, which consists of other shape objects
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CompoundShape extends BaseShape {
protected List<Shape> children = new ArrayList<>();
public CompoundShape(Shape... components) {
super(0, 0, Color.BLACK);
add(components);
}
public void add(Shape component) {
children.add(component);
}
public void add(Shape... components) {
children.addAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void remove(Shape child) {
children.remove(child);
}
public void remove(Shape... components) {
children.removeAll(Arrays.asList(components));
}
public void clear() {
children.clear();
}
@Override
public int getX() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = children.get(0).getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getX() < x) {
x = child.getX();
}
}
return x;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
if (children.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int y = children.get(0).getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.getY() < y) {
y = child.getY();
}
}
return y;
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
int maxWidth = 0;
int x = getX();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeX = child.getX() - x;
int childWidth = childsRelativeX + child.getWidth();
if (childWidth > maxWidth) {
maxWidth = childWidth;
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
int maxHeight = 0;
int y = getY();
for (Shape child : children) {
int childsRelativeY = child.getY() - y;
int childHeight = childsRelativeY + child.getHeight();
if (childHeight > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = childHeight;
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
child.move(x, y);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isInsideBounds(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void unSelect() {
super.unSelect();
for (Shape child : children) {
child.unSelect();
}
}
public boolean selectChildAt(int x, int y) {
for (Shape child : children) {
if (child.isInsideBounds(x, y)) {
child.select();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
if (isSelected()) {
enableSelectionStyle(graphics);
graphics.drawRect(getX() - 1, getY() - 1, getWidth() + 1, getHeight() + 1);
disableSelectionStyle(graphics);
}
for (Shape child : children) {
child.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
editor
editor/ImageEditor.java: Shape editor
package refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Shape;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.Border;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
public class ImageEditor {
private EditorCanvas canvas;
private CompoundShape allShapes = new CompoundShape();
public ImageEditor() {
canvas = new EditorCanvas();
}
public void loadShapes(Shape... shapes) {
allShapes.clear();
allShapes.add(shapes);
canvas.refresh();
}
private class EditorCanvas extends Canvas {
JFrame frame;
private static final int PADDING = 10;
EditorCanvas() {
createFrame();
refresh();
addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
allShapes.unSelect();
allShapes.selectChildAt(e.getX(), e.getY());
e.getComponent().repaint();
}
});
}
void createFrame() {
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
Border padding = BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(PADDING, PADDING, PADDING, PADDING);
contentPanel.setBorder(padding);
frame.setContentPane(contentPanel);
frame.add(this);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
}
public int getWidth() {
return allShapes.getX() + allShapes.getWidth() + PADDING;
}
public int getHeight() {
return allShapes.getY() + allShapes.getHeight() + PADDING;
}
void refresh() {
this.setSize(getWidth(), getHeight());
frame.pack();
}
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
allShapes.paint(graphics);
}
}
}
Demo.java: Client code
package refactoring_guru.composite.example;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.editor.ImageEditor;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Circle;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.CompoundShape;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Dot;
import refactoring_guru.composite.example.shapes.Rectangle;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImageEditor editor = new ImageEditor();
editor.loadShapes(
new Circle(10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE),
new CompoundShape(
new Circle(110, 110, 50, Color.RED),
new Dot(160, 160, Color.RED)
),
new CompoundShape(
new Rectangle(250, 250, 100, 100, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 240, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(240, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 360, Color.GREEN),
new Dot(360, 240, Color.GREEN)
)
);
}
}
OutputDemo.png: Execution result