Stan w języku TypeScript
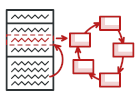
Stan to behawioralny wzorzec projektowy pozwalający zmieniać zachowanie obiektu w odpowiedzi na zmianę jego wewnętrznego stanu.
Wzorzec Stan zakłada ekstrakcję zachowań odnoszących się do stanu obiektu do osobnych klas odpowiadających jego poszczególnym stanom. Pierwotny obiekt wówczas deleguje pracę instancjom tych klas, zamiast wykonywać ją samodzielnie.
Złożoność:
Popularność:
Przykłady użycia: Wzorzec Stan jest powszechnie stosowany w kodzie TypeScript w celu konwersji obszernych maszyn stanów opartych na instrukcji switch w obiekty.
Identyfikacja: Wzorzec Stan można poznać po obecności metod zmieniających swoje zachowanie zależnie od stanu obiektu, sterowanego z zewnątrz.
Przykład koncepcyjny
Poniższy przykład ilustruje strukturę wzorca Stan ze szczególnym naciskiem na następujące kwestie:
- Z jakich składa się klas?
- Jakie role pełnią te klasy?
- W jaki sposób elementy wzorca są ze sobą powiązane?
index.ts: Przykład koncepcyjny
/**
* The Context defines the interface of interest to clients. It also maintains a
* reference to an instance of a State subclass, which represents the current
* state of the Context.
*/
class Context {
/**
* @type {State} A reference to the current state of the Context.
*/
private state: State;
constructor(state: State) {
this.transitionTo(state);
}
/**
* The Context allows changing the State object at runtime.
*/
public transitionTo(state: State): void {
console.log(`Context: Transition to ${(<any>state).constructor.name}.`);
this.state = state;
this.state.setContext(this);
}
/**
* The Context delegates part of its behavior to the current State object.
*/
public request1(): void {
this.state.handle1();
}
public request2(): void {
this.state.handle2();
}
}
/**
* The base State class declares methods that all Concrete State should
* implement and also provides a backreference to the Context object, associated
* with the State. This backreference can be used by States to transition the
* Context to another State.
*/
abstract class State {
protected context: Context;
public setContext(context: Context) {
this.context = context;
}
public abstract handle1(): void;
public abstract handle2(): void;
}
/**
* Concrete States implement various behaviors, associated with a state of the
* Context.
*/
class ConcreteStateA extends State {
public handle1(): void {
console.log('ConcreteStateA handles request1.');
console.log('ConcreteStateA wants to change the state of the context.');
this.context.transitionTo(new ConcreteStateB());
}
public handle2(): void {
console.log('ConcreteStateA handles request2.');
}
}
class ConcreteStateB extends State {
public handle1(): void {
console.log('ConcreteStateB handles request1.');
}
public handle2(): void {
console.log('ConcreteStateB handles request2.');
console.log('ConcreteStateB wants to change the state of the context.');
this.context.transitionTo(new ConcreteStateA());
}
}
/**
* The client code.
*/
const context = new Context(new ConcreteStateA());
context.request1();
context.request2();
Output.txt: Wynik działania
Context: Transition to ConcreteStateA.
ConcreteStateA handles request1.
ConcreteStateA wants to change the state of the context.
Context: Transition to ConcreteStateB.
ConcreteStateB handles request2.
ConcreteStateB wants to change the state of the context.
Context: Transition to ConcreteStateA.