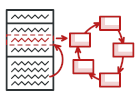
Стан на PHP
Стан — це поведінковий патерн, що дозволяє динамічно змінювати поведінку об’єкта при зміні його стану.
Поведінки, які залежать від стану, переїзджають в окремі класи. Початковий клас зберігає посилання на один з таких об’єктів-станів та делегує йому роботу.
Складність:
Популярність:
Застосування: Патерн Стан здебільшого використовують для перетвореннягроміздких стейт-машин, побудованих на операторах switch, в об’єкти.
Ознаки застосування патерна: Методи класу делегують роботу одному вкладеному об’єктові.
Концептуальний приклад
Цей приклад показує структуру патерна Стан, а саме — з яких класів він складається, які ролі ці класи виконують і як вони взаємодіють один з одним.
Після ознайомлення зі структурою, вам буде легше сприймати наступний приклад, що розглядає реальний випадок використання патерна в світі PHP.
index.php: Приклад структури патерна
<?php
namespace RefactoringGuru\State\Conceptual;
/**
* The Context defines the interface of interest to clients. It also maintains a
* reference to an instance of a State subclass, which represents the current
* state of the Context.
*/
class Context
{
/**
* @var State A reference to the current state of the Context.
*/
private $state;
public function __construct(State $state)
{
$this->transitionTo($state);
}
/**
* The Context allows changing the State object at runtime.
*/
public function transitionTo(State $state): void
{
echo "Context: Transition to " . get_class($state) . ".\n";
$this->state = $state;
$this->state->setContext($this);
}
/**
* The Context delegates part of its behavior to the current State object.
*/
public function request1(): void
{
$this->state->handle1();
}
public function request2(): void
{
$this->state->handle2();
}
}
/**
* The base State class declares methods that all Concrete State should
* implement and also provides a backreference to the Context object, associated
* with the State. This backreference can be used by States to transition the
* Context to another State.
*/
abstract class State
{
/**
* @var Context
*/
protected $context;
public function setContext(Context $context)
{
$this->context = $context;
}
abstract public function handle1(): void;
abstract public function handle2(): void;
}
/**
* Concrete States implement various behaviors, associated with a state of the
* Context.
*/
class ConcreteStateA extends State
{
public function handle1(): void
{
echo "ConcreteStateA handles request1.\n";
echo "ConcreteStateA wants to change the state of the context.\n";
$this->context->transitionTo(new ConcreteStateB());
}
public function handle2(): void
{
echo "ConcreteStateA handles request2.\n";
}
}
class ConcreteStateB extends State
{
public function handle1(): void
{
echo "ConcreteStateB handles request1.\n";
}
public function handle2(): void
{
echo "ConcreteStateB handles request2.\n";
echo "ConcreteStateB wants to change the state of the context.\n";
$this->context->transitionTo(new ConcreteStateA());
}
}
/**
* The client code.
*/
$context = new Context(new ConcreteStateA());
$context->request1();
$context->request2();
Output.txt: Результат виконання
Context: Transition to RefactoringGuru\State\Conceptual\ConcreteStateA.
ConcreteStateA handles request1.
ConcreteStateA wants to change the state of the context.
Context: Transition to RefactoringGuru\State\Conceptual\ConcreteStateB.
ConcreteStateB handles request2.
ConcreteStateB wants to change the state of the context.
Context: Transition to RefactoringGuru\State\Conceptual\ConcreteStateA.
Життєвий приклад
У цьому прикладі патерн Стан використовується для представлення різних станів Рахунку. Цей підхід дозволяє реалізувати різні перевірки умов при переході рахунку з одного стану в інший, а також інкапсулювати логіку кожного стану в окремому класі.
index.php: Приклад структури патерна
<?php
namespace RefactoringGuru\State\RealWorld;
/**
* State Design Pattern
*
* Intent: lets an object alter its behavior when its internal state changes. It
* appears as if the object changed its class.
*/
/**
* Invoice State Interface
*
* This interface defines the contract that all invoice states must implement.
* It represents the State interface in the State pattern, ensuring that all
* concrete states provide implementations for all possible events/transitions.
*
* The interface defines all possible events that can occur in the invoice
* lifecycle, regardless of whether a particular state can handle them. This
* approach ensures consistency across all states and makes the system more
* maintainable.
*/
interface InvoiceState
{
public function finalize(): void;
public function pay(): void;
public function cancel(): void;
public function void(): void;
public function getName(): string;
}
/**
* Abstract Base State class
*
* This abstract class implements the InvoiceState interface and provides
* default implementations for all state transition methods. The default
* behavior is to throw exceptions for invalid transitions, following the "fail-
* fast" principle.
*
* This approach allows concrete states to only override the methods for
* transitions they actually support, keeping the code clean and focused. Any
* attempt to perform an invalid transition will result in a clear exception
* rather than silent failure.
*
* The abstract class also maintains a reference to the context (Invoice)
* object, which is needed for performing state transitions.
*/
abstract class BaseInvoiceState implements InvoiceState
{
/**
* Reference to the context object (Invoice)
*
* Each state needs access to the context to perform state transitions.
* This creates a bidirectional relationship between the state and context.
*/
protected $invoice;
public function __construct(Invoice $invoice)
{
$this->invoice = $invoice;
}
/**
* Default implementation for finalize event
*
* By default, finalize is not allowed in most states. Only states that
* support this transition will override this method.
*
* @throws InvalidStateTransitionException
*/
public function finalize(): void
{
throw new InvalidStateTransitionException("Cannot finalize invoice in " . $this->getName() . " state");
}
/**
* Default implementation for pay event
*
* By default, payment is not allowed in most states. Only states that
* support this transition will override this method.
*
* @throws InvalidStateTransitionException
*/
public function pay(): void
{
throw new InvalidStateTransitionException("Cannot pay invoice in " . $this->getName() . " state");
}
/**
* Default implementation for cancel event
*
* By default, cancellation is not allowed in most states. Only states that
* support this transition will override this method.
*
* @throws InvalidStateTransitionException
*/
public function cancel(): void
{
throw new InvalidStateTransitionException("Cannot cancel invoice in " . $this->getName() . " state");
}
/**
* Default implementation for void event
*
* By default, voiding is not allowed in most states. Only states that
* support this transition will override this method.
*
* @throws InvalidStateTransitionException
*/
public function void(): void
{
throw new InvalidStateTransitionException("Cannot void invoice in " . $this->getName() . " state");
}
/**
* Abstract method to get the state name
*
* Each concrete state must implement this method to return its name. This
* is used for logging, debugging, and display purposes.
*
* @return string The name of the current state
*/
abstract public function getName(): string;
}
/**
* Each Concrete State corresponds to a specific state.
*
* This Concrete State Represents a draft invoice.
*
* This is the initial state of every invoice. In this state, the invoice is
* still being prepared and can only be finalized to move to the Open state. No
* other operations are allowed in this state.
*/
class DraftInvoiceState extends BaseInvoiceState
{
/**
* Handle finalize event
*
* This is the only valid transition from Draft state. When an invoice is
* finalized, it transitions to the Open state where it can be paid, voided,
* or cancelled.
*/
public function finalize(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} finalized - changing from Draft to Open\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new OpenInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
public function getName(): string
{
return 'draft';
}
}
/**
* This Concrete State Represents an open invoice.
*
* This state represents an invoice that has been finalized and is ready for
* processing. From this state, the invoice can be:
* - Paid (moves to Paid state)
* - Voided (moves to Void state)
* - Cancelled (moves to Uncollectable state)
*/
class OpenInvoiceState extends BaseInvoiceState
{
/**
* Handle pay event
*
* When payment is received, the invoice transitions to the Paid state. This
* is a terminal state - no further operations are allowed.
*/
public function pay(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} paid - changing from Open to Paid\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new PaidInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
/**
* Handle void event
*
* When an invoice is voided, it transitions to the Void state. This is a
* terminal state - no further operations are allowed.
*/
public function void(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} voided - changing from Open to Void\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new VoidInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
/**
* Handle cancel event
*
* When an invoice is cancelled, it transitions to the Uncollectable state.
* From Uncollectable, the invoice can still be paid or voided.
*/
public function cancel(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} cancelled - changing from Open to Uncollectable\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new UncollectableInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
public function getName(): string
{
return 'open';
}
}
/**
* This Concrete State Represents a paid invoice.
*
* This is a terminal state representing a paid invoice. Once an invoice is
* paid, no further state transitions are allowed. All event methods use the
* default implementation which throws exceptions.
*/
class PaidInvoiceState extends BaseInvoiceState
{
public function getName(): string
{
return 'paid';
}
}
/**
* This Concrete State Represents a void invoice.
*
* This is a terminal state representing a voided invoice. Once an invoice is
* voided, no further state transitions are allowed. All event methods use the
* default implementation which throws exceptions.
*/
class VoidInvoiceState extends BaseInvoiceState
{
public function getName(): string
{
return 'void';
}
}
/**
* This Concrete State Represents a collectable invoice.
*
* This state represents an invoice that has been cancelled but can still be
* recovered. From this state, the invoice can be:
* - Paid (moves to Paid state)
* - Voided (moves to Void state)
*
* This provides a way to handle invoices that were cancelled but later can be
* collected or definitively written off.
*/
class UncollectableInvoiceState extends BaseInvoiceState
{
/**
* Handle pay event
*
* Even though the invoice was cancelled, payment can still be received.
* This transitions the invoice to the Paid state.
*/
public function pay(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} paid - changing from Uncollectable to Paid\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new PaidInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
/**
* Handle void event
*
* If the invoice is definitively uncollectable, it can be voided. This
* transitions the invoice to the Void state.
*/
public function void(): void
{
echo "Invoice #{$this->invoice->getId()} voided - changing from Uncollectable to Void\n";
$this->invoice->setState(new VoidInvoiceState($this->invoice));
}
public function getName(): string
{
return 'uncollectable';
}
}
/**
* Context class - Invoice
*
* This is the context class in the State pattern. It maintains a reference to
* the current state object and delegates all state-specific behavior to the
* current state. The context is unaware of the specific state classes and
* interacts with them through the abstract InvoiceState interface.
*
* The context also maintains the invoice's data (id, amount, etc.) that remains
* constant regardless of the state.
*/
class Invoice
{
private $id;
private $amount;
/**
* Current state object
*
* This is the key component of the State pattern. The context maintains a
* reference to the current state object and delegates all state-specific
* operations to this object.
*
* @var InvoiceState
*/
private $state;
private $createdAt;
/**
* Constructor
*
* Creates a new invoice. The invoice always starts in the Draft state as
* per business requirements.
*/
public function __construct(int $id, float $amount)
{
$this->id = $id;
$this->amount = $amount;
$this->createdAt = new \DateTime();
// Initial state is draft This is where the State pattern begins - we
// set the initial state
$this->state = new DraftInvoiceState($this);
}
public function getId(): int
{
return $this->id;
}
/**
* Set the current state
*
* This method is called by state objects to transition to a new state. It's
* the mechanism that allows the State pattern to work - states can change
* the context's state by calling this method.
*
* @param InvoiceState $state The new state object
*/
public function setState(InvoiceState $state)
{
$this->state = $state;
}
/**
* Get the current state object
*
* @return InvoiceState
*/
public function getState(): InvoiceState
{
return $this->state;
}
/**
* Get the current state name
*
* This is a convenience method that delegates to the current state object.
*
* @return string
*/
public function getStateName(): string
{
return $this->state->getName();
}
/**
* Event method: finalize
*
* This method delegates the finalize operation to the current state. This
* is the core of the State pattern - the context doesn't know how to handle
* the operation, so it delegates to the current state.
*/
public function finalize()
{
$this->state->finalize();
}
/**
* Event method: pay
*
* This method delegates the pay operation to the current state. The
* behavior will vary depending on the current state.
*/
public function pay()
{
$this->state->pay();
}
/**
* Event method: cancel
*
* This method delegates the cancel operation to the current state. The
* behavior will vary depending on the current state.
*/
public function cancel()
{
$this->state->cancel();
}
/**
* Event method: void
*
* This method delegates the void operation to the current state. The
* behavior will vary depending on the current state.
*/
public function void()
{
$this->state->void();
}
/**
* Get invoice information
*
* Returns an array with all invoice information including current state.
* This is useful for debugging, logging, or API responses.
*
* @return array
*/
public function getInfo(): array
{
return [
'id' => $this->id,
'amount' => $this->amount,
'state' => $this->getStateName(),
'created_at' => $this->createdAt->format('Y-m-d H:i:s')
];
}
}
/**
* Custom exception for invalid state transitions
*
* This exception is thrown when an invalid state transition is attempted. It
* provides clear error messages about what transition was attempted and why it
* failed.
*/
class InvalidStateTransitionException extends \Exception
{
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param string $message Error message
* @param int $code Error code
* @param \Exception|null $previous Previous exception
*/
public function __construct($message = "", $code = 0, \Exception $previous = null)
{
parent::__construct($message, $code, $previous);
}
}
/**
* ============================================================================
* USAGE EXAMPLE AND DEMONSTRATION
* ============================================================================
*
* The following code demonstrates how to use the State pattern implementation
* with various scenarios that show all possible state transitions.
*/
try {
echo "=== Invoice State Pattern Demo ===\n\n";
// Create a new invoice (starts in draft state)
$invoice = new Invoice(1001, 1500.00);
echo "Created invoice: " . json_encode($invoice->getInfo()) . "\n\n";
// Scenario 1: Draft -> Open -> Paid
echo "--- Scenario 1: Draft -> Open -> Paid ---\n";
$invoice->finalize(); // Draft -> Open
echo "Current state: " . $invoice->getStateName() . "\n";
$invoice->pay(); // Open -> Paid
echo "Current state: " . $invoice->getStateName() . "\n";
// Try to pay again (should fail)
try {
$invoice->pay();
} catch (InvalidStateTransitionException $e) {
echo "Expected error: " . $e->getMessage() . "\n";
}
echo "\n--- Scenario 2: Draft -> Open -> Void ---\n";
$invoice2 = new Invoice(1002, 750.00);
$invoice2->finalize(); // Draft -> Open
$invoice2->void(); // Open -> Void
echo "Invoice 2 state: " . $invoice2->getStateName() . "\n";
echo "\n--- Scenario 3: Draft -> Open -> Uncollectable -> Paid ---\n";
$invoice3 = new Invoice(1003, 2000.00);
$invoice3->finalize(); // Draft -> Open
$invoice3->cancel(); // Open -> Uncollectable
echo "Invoice 3 state: " . $invoice3->getStateName() . "\n";
$invoice3->pay(); // Uncollectable -> Paid
echo "Invoice 3 final state: " . $invoice3->getStateName() . "\n";
echo "\n--- Scenario 4: Draft -> Open -> Uncollectable -> Void ---\n";
$invoice4 = new Invoice(1004, 500.00);
$invoice4->finalize(); // Draft -> Open
$invoice4->cancel(); // Open -> Uncollectable
$invoice4->void(); // Uncollectable -> Void
echo "Invoice 4 final state: " . $invoice4->getStateName() . "\n";
echo "\n--- Error Scenario: Invalid transition ---\n";
$invoice5 = new Invoice(1005, 300.00);
try {
$invoice5->pay(); // Try to pay draft invoice (should fail)
} catch (InvalidStateTransitionException $e) {
echo "Expected error: " . $e->getMessage() . "\n";
}
echo "\n--- State Information ---\n";
echo "Invoice 1: " . json_encode($invoice->getInfo()) . "\n";
echo "Invoice 2: " . json_encode($invoice2->getInfo()) . "\n";
echo "Invoice 3: " . json_encode($invoice3->getInfo()) . "\n";
echo "Invoice 4: " . json_encode($invoice4->getInfo()) . "\n";
echo "Invoice 5: " . json_encode($invoice5->getInfo()) . "\n";
} catch (InvalidStateTransitionException $e) {
echo "Error: " . $e->getMessage() . "\n";
}
Output.txt: Результат виконання
=== Invoice State Pattern Demo ===
Created invoice: {"id":1001,"amount":1500,"state":"draft","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}
--- Scenario 1: Draft -> Open -> Paid ---
Invoice #1001 finalized - changing from Draft to Open
Current state: open
Invoice #1001 paid - changing from Open to Paid
Current state: paid
Expected error: Cannot pay invoice in paid state
--- Scenario 2: Draft -> Open -> Void ---
Invoice #1002 finalized - changing from Draft to Open
Invoice #1002 voided - changing from Open to Void
Invoice 2 state: void
--- Scenario 3: Draft -> Open -> Uncollectable -> Paid ---
Invoice #1003 finalized - changing from Draft to Open
Invoice #1003 cancelled - changing from Open to Uncollectable
Invoice 3 state: uncollectable
Invoice #1003 paid - changing from Uncollectable to Paid
Invoice 3 final state: paid
--- Scenario 4: Draft -> Open -> Uncollectable -> Void ---
Invoice #1004 finalized - changing from Draft to Open
Invoice #1004 cancelled - changing from Open to Uncollectable
Invoice #1004 voided - changing from Uncollectable to Void
Invoice 4 final state: void
--- Error Scenario: Invalid transition ---
Expected error: Cannot pay invoice in draft state
--- State Information ---
Invoice 1: {"id":1001,"amount":1500,"state":"paid","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}
Invoice 2: {"id":1002,"amount":750,"state":"void","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}
Invoice 3: {"id":1003,"amount":2000,"state":"paid","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}
Invoice 4: {"id":1004,"amount":500,"state":"void","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}
Invoice 5: {"id":1005,"amount":300,"state":"draft","created_at":"2025-07-12 13:14:15"}